This blog explains Dog Eczema, its symptoms, causes, risk factors, and management & treatment by homeopathic medicines.
Eczema is a skin condition characterized by inflammation, redness, itching, and dryness.
It is a common condition that can affect both humans and animals, including dogs.
Dog eczema, also known as canine atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that affects dogs of all breeds and ages.
Types of Dog Eczema:
Dog eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that can be caused by a variety of factors. Different types of eczema can affect dogs, each with its specific causes and symptoms.
The following are some of the most common types of eczema in dogs:
1. Contact dermatitis:
This type of eczema is caused by contact with irritants or allergens, such as chemicals in cleaning products, flea and tick treatments, or plants. Symptoms can include redness, itching, and inflammation of the skin, often in the areas of contact.
2. Atopic dermatitis:
This is a hereditary type of eczema that is caused by a genetic predisposition to allergies. Dogs with atopic dermatitis can be allergic to a variety of environmental allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, or mold.
Symptoms can include itching, redness, and inflammation of the skin, particularly around the ears, paws, and face.

3. Food allergies:
Some dogs can develop eczema as a result of food allergies. Common allergens include beef, chicken, dairy, and wheat. Symptoms can include itching, redness, and inflammation of the skin, particularly around the face, ears, and paws.
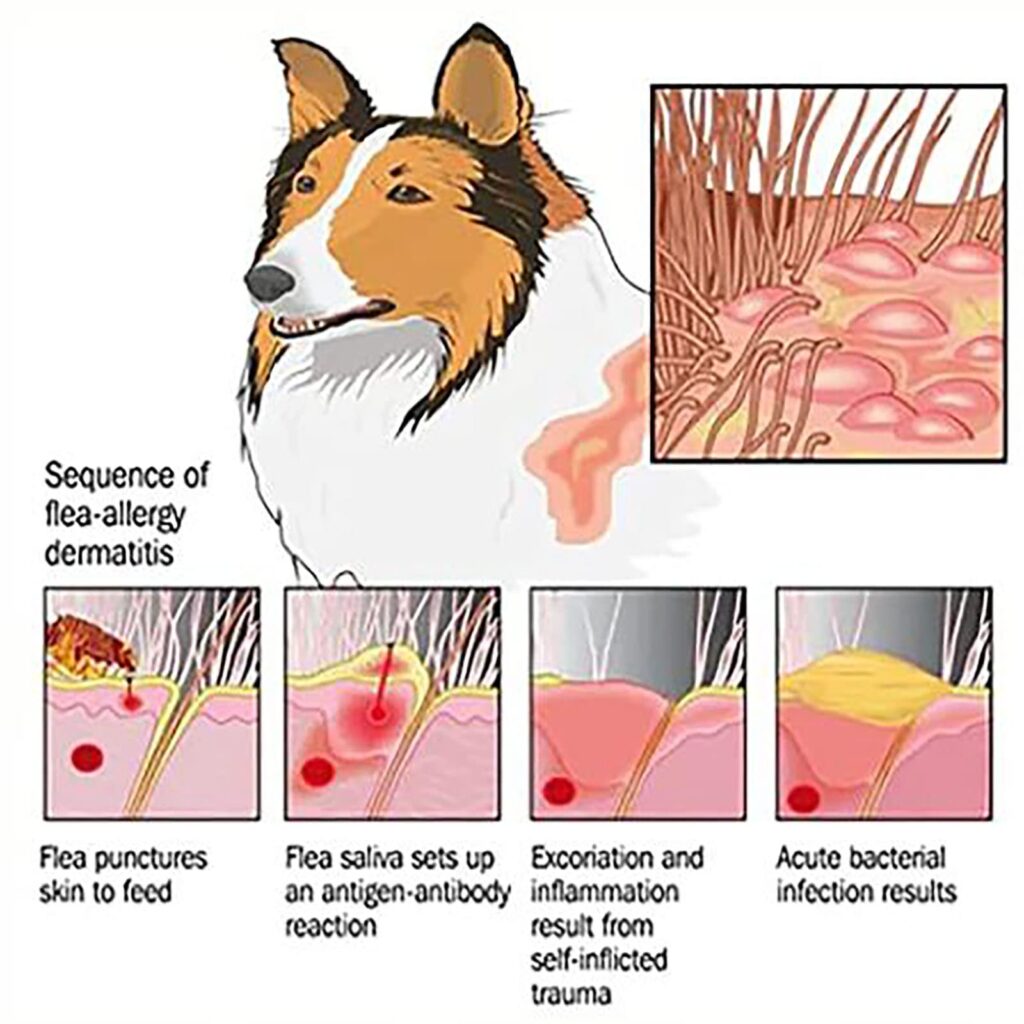
4. Flea allergy dermatitis:
This type of eczema is caused by an allergic reaction to flea saliva. Symptoms can include itching, redness, and inflammation of the skin, particularly around the tail, hindquarters, and abdomen.
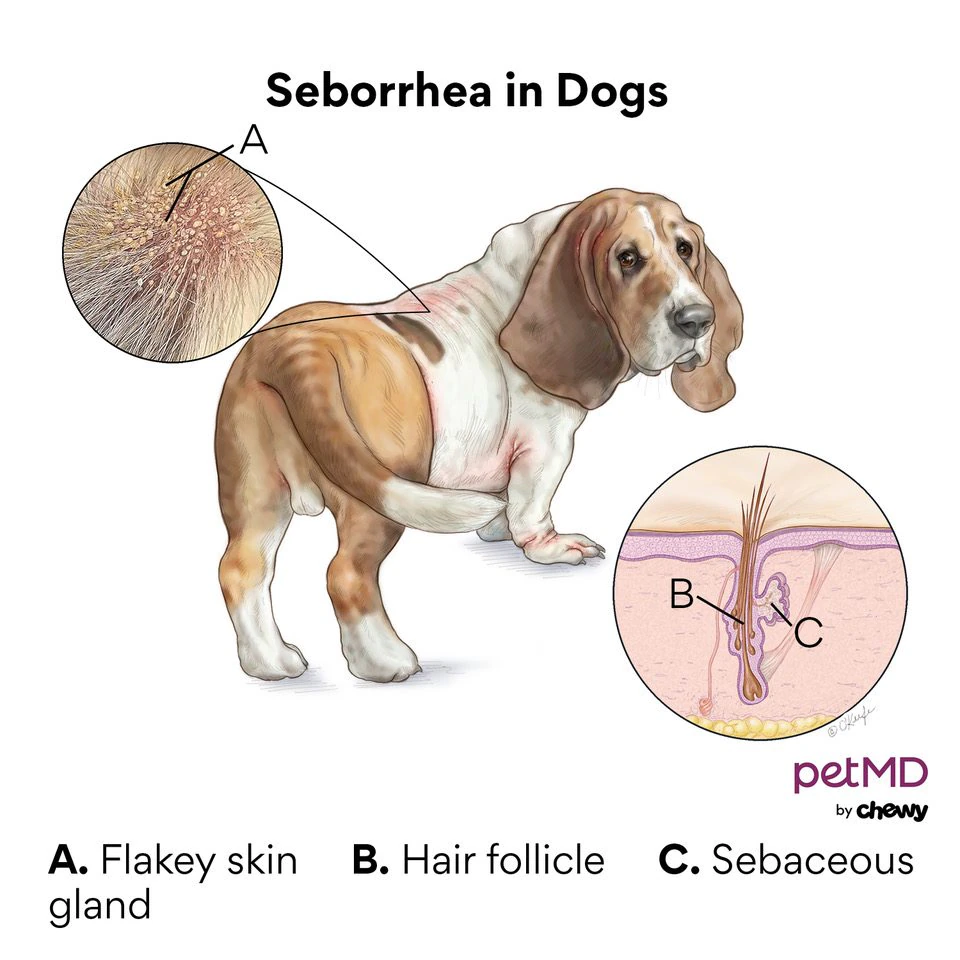
5. Seborrheic dermatitis:
This type of eczema is caused by an overproduction of sebum, the oily substance that protects the skin. Symptoms can include flaky, scaly skin, and an oily or greasy appearance.
6. Neurogenic dermatitis:
This type of eczema is caused by a psychological condition, such as stress or anxiety. Symptoms can include intense itching, hair loss, and skin damage due to excessive licking or scratching.
Causes of Dog Eczema:
The exact cause of dog eczema is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Here are some of the common causes of dog eczema:
1. Genetics:
Some dogs are genetically predisposed to develop eczema. Breeds such as bulldogs, terriers, and retrievers are more likely to develop atopic dermatitis.
2. Environmental Allergens:
Dogs can develop an allergic reaction to environmental allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and mold.
3. Flea Allergy Dermatitis:
Fleas are a common cause of eczema in dogs. Flea bites can cause an allergic reaction, which can lead to itching, redness, and inflammation.
4. Food Allergies:
Certain foods can cause an allergic reaction in some dogs, leading to the development of eczema. Common allergenic foods include beef, dairy, chicken, and wheat.
5. Irritants:
Certain substances such as detergents, chemicals, and plants can cause irritation and inflammation of the skin, leading to the development of eczema.
Symptoms of Dog Eczema:
Dog eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that causes inflammation, itching, and discomfort.
The symptoms of dog eczema can vary depending on the severity of the condition, but the following are some common signs to look out for:
1. Itching:
One of the most common symptoms of dog eczema is intense itching. The dog may scratch, bite, or lick at the affected areas, which can lead to further skin damage and secondary infections.
2. Redness:
The affected skin may appear red, inflamed, and irritated. This is often accompanied by small bumps or pustules.
3. Dryness:
The affected skin may be dry, scaly, and flaky. The skin may also feel rough and have a thickened texture.
4. Hair loss:
Chronic itching and scratching can lead to hair loss, particularly in the affected areas. The skin may also appear thin and fragile.
5. Discoloration:
In some cases, the affected skin may become darker or lighter than the surrounding skin.
6. Odour:
The skin may have a foul odour due to secondary bacterial infections.
7. Ear infections:
Dogs with eczema may be more prone to ear infections due to their immune system’s weakened response.
8. Licking and chewing:
Dogs with eczema may lick and chew at their paws and other parts of their body to relieve itching and discomfort.
It is important to seek veterinary care if your dog is exhibiting any of these symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further complications and improve the quality of life for your dog.
If left untreated, eczema can lead to chronic skin infections, scarring, and permanent skin damage. Your veterinarian can provide personalized recommendations for managing the symptoms and treating the underlying cause of eczema in your dog.
Risk Factors of dog Eczema:
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of a dog developing eczema. Some of the common risk factors include:
1. Breed:
Certain breeds of dogs are more susceptible to eczema than others. For example, breeds such as bulldogs, terriers, and retrievers are more prone to atopic dermatitis.
2. Age:
Eczema is more common in dogs under the age of three. However, it can occur at any age.
3. Gender:
Female dogs are more likely to develop eczema than male dogs.
4. Environmental factors:
Exposure to environmental allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and mold can increase the risk of developing eczema.
5. Poor nutrition:
A diet lacking essential nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E can weaken the immune system, making dogs more susceptible to eczema.
6. Parasites:
Parasites such as fleas and mites can irritate the skin, leading to the development of eczema.
7. Stress:
Stress can weaken the immune system, making dogs more susceptible to eczema.
8. Genetics:
Some dogs are genetically predisposed to developing eczema. If a dog’s parents or siblings have eczema, the dog is more likely to develop the condition.
It is important to note that while these risk factors increase the likelihood of a dog developing eczema, they do not guarantee that a dog will develop the condition.
Proper care and management, including regular veterinary checkups and a balanced diet, can help reduce the risk of eczema in dogs.
Diagnosis of Dog Eczema:
Diagnosing dog eczema can be challenging, as the symptoms of eczema can be similar to those of other skin conditions. A veterinarian will typically perform a physical examination of the dog’s skin and may also perform additional tests to determine the underlying cause of eczema.
During a physical examination, the veterinarian will look for signs of redness, inflammation, itching, and dryness on the dog’s skin. They may also examine the dog’s ears, paws, and anal area, as these are common areas affected by eczema.
In addition to a physical examination, the veterinarian may also perform skin tests to determine the underlying cause of eczema.
These tests may include:
Intradermal skin testing:
This involves injecting a small number of allergens under the dog’s skin to see if an allergic reaction occurs.
Blood tests:
These tests can help determine if the dog has an allergic reaction to certain foods or environmental allergens.
Skin biopsy:
A skin biopsy involves taking a small sample of the affected skin and examining it under a microscope. This can help determine the underlying cause of eczema.
If the eczema is caused by an underlying condition such as a food allergy, the veterinarian may recommend an elimination diet to identify the allergenic food.
This involves removing certain foods from the dog’s diet and gradually reintroducing them to see if eczema improves or worsens.
It is important to seek veterinary care if your dog is experiencing symptoms of eczema, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further complications.
Treatment for dog eczema typically involves managing the symptoms and addressing the underlying cause. This may include topical medications, dietary changes, and allergy shots.
Your veterinarian can provide personalized recommendations for your dog based on their individual needs and condition.
Dog Eczema Treatment:
The treatment of dog eczema will depend on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. It is important to seek veterinary care to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The following are some of the treatment options for dog eczema:
1. Topical medications:
The use of topical medications such as corticosteroids, antihistamines, and immunomodulators can help relieve the symptoms of eczema. These medications are available in various forms such as creams, ointments, and sprays.
2. Dietary changes:
If the eczema is caused by a food allergy, the veterinarian may recommend an elimination diet to identify and remove the allergenic food from the dog’s diet. This can help reduce the severity of the symptoms and prevent future flare-ups.
3. Allergy shots:
In cases where the eczema is caused by environmental allergens, allergy shots can be used to desensitize the dog’s immune system. This can help reduce the severity of the symptoms and prevent future flare-ups.
4. Antibiotics:
If eczema has led to a bacterial infection, the veterinarian may prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection.
5. Bathing:
Regular bathing with a gentle shampoo can help remove allergens and irritants from the dog’s skin and reduce the severity of the symptoms.
6. Moisturizing:
Moisturizing the affected areas with a moisturizer or emollient can help reduce dryness and itching.
In severe cases, systemic medications may be needed. This may include oral steroids or immunosuppressive drugs.
It is important to note that some treatments for eczema can have side effects and long-term use of corticosteroids can lead to adverse health effects. Therefore, it is important to follow your veterinarian’s instructions and monitor your dog closely for any side effects.
In addition to medical treatment, it is important to identify and avoid triggers that may cause eczema flare-ups. This may include avoiding certain foods, using hypoallergenic bedding, and reducing exposure to environmental allergens such as pollen and dust.
Homeopathy Treatment for Dog Eczema:
Homeopathy is a holistic approach to healthcare that involves using natural remedies to stimulate the body’s natural healing process. It can be an effective management option for dog eczema, particularly when used in conjunction with traditional veterinary care.
In addition to homeopathic remedies, several lifestyle changes can be made to manage the symptoms of dog eczema.
These include:
Diet: Dogs with eczema may benefit from a diet that is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can help to reduce inflammation in the body. Foods that are high in omega-3s include salmon, sardines, and flaxseed oil. Additionally, some dogs may be allergic to certain foods, such as beef, chicken, dairy, and wheat. Identifying and eliminating these allergens from the diet can help to reduce eczema symptoms.
Bathing: Regular bathing can help to remove allergens and irritants from the skin and reduce itching. It is important to use a gentle, hypoallergenic shampoo that is specifically formulated for dogs with sensitive skin. After bathing, the skin should be thoroughly dried to prevent moisture from accumulating.
Environmental control: Dogs with eczema may be sensitive to certain environmental allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, and mold. Limiting exposure to these allergens can help to reduce symptoms. This may involve using air filters, vacuuming regularly, and washing bedding and toys frequently.
Exercise: Regular exercise can help to reduce stress and improve overall health, which can in turn help to manage eczema symptoms. However, it is important to avoid excessive exercise or activities that may cause the dog to overheat or become dehydrated.
Emotional support: Dogs need emotional support in such health conditions. Emotional support helps them to fight against eczema.
Some common homeopathic remedies that may be used to manage the symptoms of dog eczema include:
1. Arnica: Useful for crops of a small eruption.
Arnica is useful for treating small black and blue colour skin eruptions on the skin. Eczema is triggered by traumatic injury.
Dose and Potency: Arnica mother tincture 5 drops two times a day. Use arnica lotion externally on the skin of the dog.
2. Arsenic album: For dry, rough, and withered skin.
Arsenic Album remedy is useful for dry skin dog eczema. The skin tends to ulcerate. The dog is restless. This remedy has great importance in chronic eczema cases.
Dose and Potency: Arsenic alb 6C, liquid, 4 drops once a day for 3 days. Use ars alb liquid externally for skin eruption.
3. Apis mellifica: Helpful for red, swollen, and itchy skin in Dog eczema.
This remedy is made from the honeybee and can be helpful for dogs with red, swollen, and itchy skin. It is often used for eczema that is worse from heat and better from cold compresses.
Dose and Potency: Apis mellifica 6C- Liquid. 4 drops of Apis liquid, 2 times a day for 8 days.
4. Borax: Dry skin dog eczema.
This is a great remedy for unhealthy dry eczema. This is a good choice for chronic unhealed eczema on the dog’s legs.
Dose and Potency: Borax 6C, 5 drops two times a day for 15 days. Use Borax lotion externally on eczema.
5. Calendula: Useful for thick, yellowish suppuration.
This is a useful remedy for yellowish eruptions. Eczema contains old suppurative thick eruptions.
Dose and Potency: Calendula lotion 3 times a day for 15-20 days. Calendula has a great effect when used externally.
6. Sulphur: This remedy is useful to treat the tendency of dog eczema.
This remedy is made from the element sulfur and can be helpful for dogs with dry, itchy, and scaly skin. It is often used for eczema that is worse at night and better from warm baths.
Dose and Potency: Sulphur 6X, 4 drops once a day per week and use Sulphur cream externally for dog eczema.
7. Graphites: Helpful for dogs with thick and crusty eczema.
This remedy is made from graphite, a form of carbon, and can be helpful for dogs with thickened, oozing, and crusty skin. It is often used for eczema that is worse in cold weather and better from warm compresses.
Dose and Potency: Graphites 3X, 6X, 4 drops two times a day for 10 days.
8. Rhus Toxicodendron: Useful for red, swollen, and itchy dog eczema.
This remedy is made from poison ivy and can be helpful for dogs with red, swollen, and itchy skin that is worse from rest and better from motion.
Dose and Potency: Rhus tox 6 X, 4 drops two times a day for 15 days.
9. Natrum muriaticum: Useful for dry, cracked, and scaly dog eczema.
This remedy is made from sodium chloride and can be helpful for dogs with dry, cracked, and scaly skin. It is often used for eczema that is worse from emotional stress and better from rest.
Dose and Potency: Natrum mur 12X, 4 drops once a day for 15 days.
10. Silicea: Useful for chronic dry dog eczema.
This remedy is useful for old dry eczema. It also helps to reduce keloid growth.
Dose and Potency: Silicea 6X, 4 drops two times a day for 15 days. Use Silicea cream externally on the dog’s skin.
A licensed homeopathic veterinarian should be consulted before using any homeopathic remedies for dog eczema. A professional homeopathic vet will take into account the individual dog’s symptoms and overall health history to determine the most appropriate remedies and dosages.
Remember that homeopathic remedies are prescribed based on individual symptoms and characteristics.
It’s crucial to consult with a qualified homeopath for proper evaluation and personalized treatment.
Homeopathic medicines should be taken only when prescribed by a homeopathic physician. Self-medication may aggravate the original conditions.