This blog explains homeopathic remedies for arthritis, causes, symptoms, risk factors, types, management & best medicines.
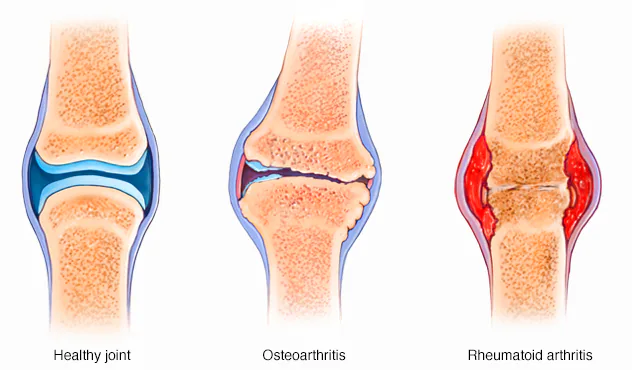
Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints. The condition defines single or multiple joint pain and inflammation.
There are two major types of arthritis, acute, and chronic that depend on the onset of diseases.
Acute arthritis is secondary to rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and viral infection.
On the contrary chronic arthritis is defined as pain and swelling of joints that persist for more than 6 weeks.
Arthritis is divided into monoarthritis (Involvement of a single joint), oligoarthritis (affects 2-4 joints or joint group like wrist), and polyarthritis (inflammation of five or more joints, joint group, all small joints or large joints).
Arthritis is mostly associated with other underlying chronic disease conditions like a viral infection- dengue, Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and Psoriasis.
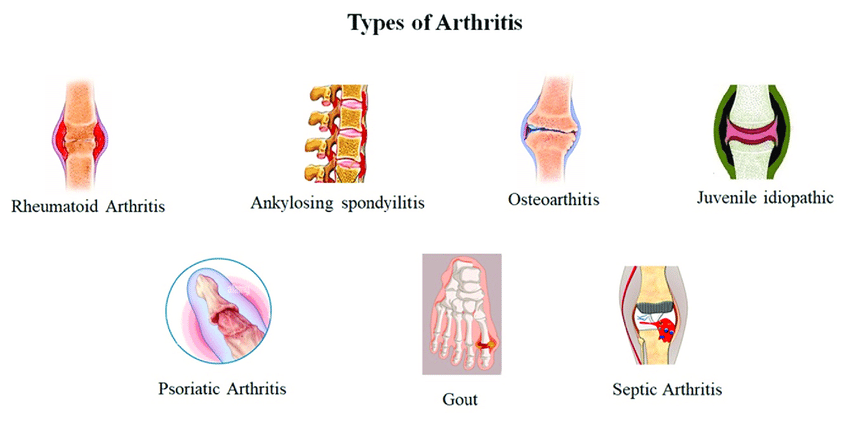
Types of Arthritis:
As mentioned above, arthritis has different types. Arthritis is divided into several types, like osteoarthritis, rheumatic arthritis, and septic arthritis depending on causative factors.
1. Osteoarthritis:
It is the most common arthritis in old age people that causes pain and major disabilities.
The most prominent features are pain with the affection of synovial fluid. The knee and hip are prominent sites of osteoarthritis.
The joint structure includes bones, cartilage, and synovial fluid. Every joint has specific bone shapes because of which those bones attach to each other and form a specific joint.
If one of the structures of joints like synovial fluid, cartilage, or bone shapes gets affected then results in joint failure.
- Cartilage: Degradation of cartilage components like aggrecan, and collagen leads to an increase in the water concentration and swelling pressure in cartilage. It makes cartilage vulnerable to load-bearing injury, cartilage loss, and decreased thickness of cartilage affects joint function and cartilage is prone to deposition of crystals of calcium phosphate and calcium pyrophosphate.
- Bone structure: Osteolysis and osteosclerosis lead to remodeling of bone. New fibrocartilage and osteophytes form at the joint. Thinning cartilage and changes in bone shapes alter the joint and increase friction and surface area.
- Synovial fluid, the protective membrane of the joint undergoes changes that lead to joint pain and disabilities.
2. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA):
This is the most common inflammatory arthritis that persists all over the world. RA course is prolonged and has intermittent exacerbation and remission of swelling, and pain of joints.
Age, genetic factors, and environmental factors are responsible for rheumatic arthritis.
RA is triggered by an infectious agent known as the RA factor.
RA is characterized by the infiltration of synovial membranes by lymphocytes, plasma cells, and macrophages.
CD4 cells, T cells, and macrophages produce pro-inflammatory cytokines which act on endothelium, synovial fibroblast, bone cells, and chondrocytes. It promotes swelling and congestion of the synovial membrane, and destruction of bone, cartilage, and soft tissues.
Sometimes RA is associated with rheumatoid nodules that consist of fibrinoid material surrounded by proliferative mononuclear cells.
3. Seronegative Spondylarthritis:
This is a group of related inflammatory joint diseases distinct from rheumatic arthritis.
Nonspecific inflammation of the synovial membrane and absence of granuloma is distinguishing features of spondylarthritis from RA.
Seronegative spondylarthritis includes a marked degree of extra synovial inflammation, affecting the joint capsule, periarticular periosteum, cartilage, and subchondral bone.
Sacroiliac joints, intervertebral and symphysis pubis are major joints that are involved in spondylarthritis.
It differentiated into ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and arthropathy associated with inflammatory bowel disease.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: It is chronic inflammatory arthritis affecting the sacroiliac joints and spine. There are no specific trigger factors but specific pathogens attack susceptible individuals.
- Reiter’s disease/ Reactive Arthritis: It affects mostly young men (Age group 16-35). This is a classic triad of non-specific urethritis, Conjunctivitis, and reactive arthritis.
- Psoriatic arthritis: Arthritis associated with the history of psoriasis.
4. Gout, Crystal associated disease:
Deposition of crystals in and around joints associated with acute inflammation of joints of the chronic syndrome.
Primary gout belongs to uric acid derived from dietary sources and from purine metabolism. Secondary gout is associated with renal impairment or chronic diuretic use.
5. Septic arthritis and osteomyelitis:
It is an infection of bone and joints. Septic arthritis is a medical emergency condition as compared to osteomyelitis.
Associated with blood infection either skin or respiratory infection. The adjacent bone joint infection causes septic arthritis, while infection of bone marrow is the primary site of osteomyelitis.
Osteomyelitis is a complication after orthopedics surgery or trauma.
Nowadays viral arthritis presents with acute polyarthritis. It includes Joint pain and swelling after viral infections like dengue and chikungunya.
Arthritis Causes:
Aging is the main factor. Genetic factors, gender/hormonal status, obesity, high bone mineral density, trauma, Joint shape-alignment, and some occupational hazards like farmers, mine workers, and football players.
Age:
Some young people are prone to reactive arthritis, while older people have osteoarthritis, osteomyelitis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Middle-aged affected by gout, rheumatic arthritis.
Gender:
Females are more prone to ankylosing spondylitis ( back pain, neck pain with stiffness). Reiter’s disease is dominant in men. Gout presents more in men and in old women.
Genetic factor:
Most of the time causative factor of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis is a hereditary pattern of the family.
Immunity factor:
Low immunity people are more susceptible to Viral arthritis, rheumatic arthritis, osteomyelitis, and infective arthritis. Respiratory infection, diabetes mellitus, viral and bacterial infection, Tuberculosis, and AIDS are responsible for reducing the immunity of patients.
In rheumatic arthritis, the RA factor plays an important role to predispose the condition to arthritis.
Trauma:
Osteoarthritis and infection of bone are secondary to trauma. Pain and swelling of joints require some time to improve their condition.
Underlying chronic diseases:
Acute joint pains are most of the time acute exacerbation of chronic conditions like diabetes, renal infection, tuberculosis, Rheumatic arthritis, osteoarthritis, psoriasis, and obesity.
Occupational causes:
Occupation or sport plays an important role in joint pain. The hip joint gets affected in farmers similarly the knee joint is in miners. Footballers face more knee osteoarthritis problems while tennis players are more prone to ankle joint pain and tennis elbow.
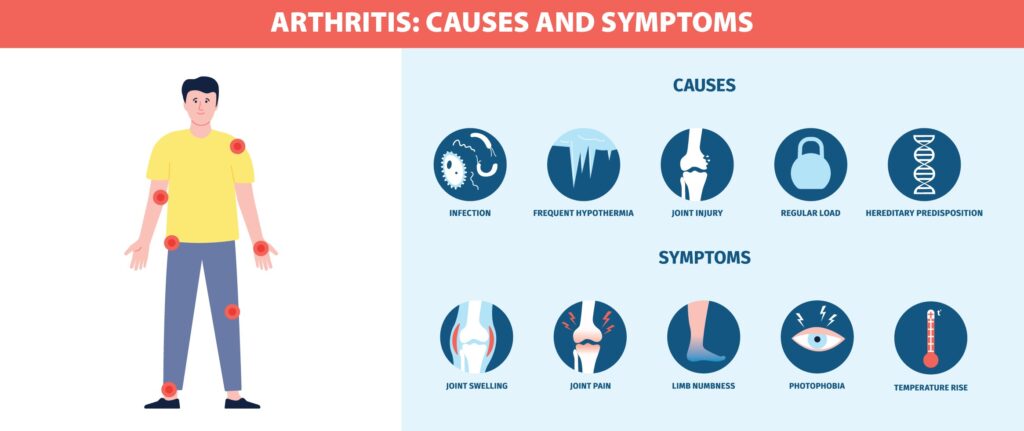
Arthritis Symptoms:
Arthritis Pain and swelling of single or multiple joints, and stiffness are more common symptoms of arthritis. According to the type of arthritis symptoms vary.
Only a single joint is involved in monoarthritis, 2-4 joints or joint groups like the wrist are involved in oligoarthritis and five or more joints have pain during polyarthritis.
In acute joint pain, the pain lasts for 2-3 weeks with underlying causes such as rheumatoid arthritis, pseudogout, infection of the bone, cartilage or synovial fluid infection, viral infection, and trauma.
During chronic arthritis, the pain lasts for more than 6 weeks. A patient has pain, and stiffness during movements. Rheumatic arthritis, gout, and osteoarthritis are chronic joint diseases.
Rheumatic arthritis, osteoarthritis, and gout have characteristic symptoms:
Osteoarthritis:
- Hip, knee, and interphalangeal joints are prominent sites of pain. Usually, one or few joints have pain.
- Slow onset of symptoms over months to years in people who are above 45 years of age.
- Patients may state some good days without pain alternate with worse days with pain.
- Pain and functional restrictions, and morning stiffness are characteristic of osteoarthritis.
- Pain is worse after movement and rest relieves pain.
- Osteoarthritis very few times is associated with swelling of bone around joints or deformity without instability.
- A patient complains of weakness of muscles, tenderness, and mild synovitis.
- Knee osteoarthritis patients have crepitus sounds, palpable surface, tenderness, and swelling around the joint with a jerky, asymmetric walking.
- Hip osteoarthritis patients have deep pain in the anterior groin region that radiates to the buttock, anterolateral thigh, knee, or shin. Obesity may lead to the rapid progression of the disease.
Rheumatic Arthritis:
- The patient complains of pain, swelling, and stiffness in small joints of hands, feet, and wrists.
- RA differentiates from other acute arthritis if the pain in joints persists for more than 6 weeks.
- Typical features of hands: symmetrical swelling of metacarpophalangeal joints and proximal part of interphalangeal joints. Tenderness with pressure and edema is present.
- Repeated small attacks of rheumatoid arthritis lead to deformity of joints of the ankle, hand, fingers, and wrist e.g. Z deformity of thumb, Swan Neck deformity, Cock-up toe deformity. The flat foot is also part of chronic rheumatoid arthritis.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is associated with muscle wasting, weight loss, loss of appetite, anemia, and fatigue. Acute relapse of RA has a fever with pain.
Gout:
- Severe pain with swelling in distal joints and in metatarsophalangeal joints, especially big toes.
- Gout has a rapid onset, within 2-6 hours patients may feel worse pain than ever.
- Extreme tenderness and swelling of joint with red, shiny skin.
- Acute pain subsides slowly within 10-14 days and remains pruritic rash behind.
- Chronic gout has a slow onset from the first acute attack of gout pain. It has been 10 years since the first attack.
- Progressive renal disease and uric acid diathesis lead to the rapid progression of chronic gout.
Risk Factors for Arthritis:
As discussed, earlier age, genetic disposition, and underlying chronic diseases increase arthritic conditions.
Age:
Middle-age people are prone to gout, and rheumatic arthritis while older ones suffer from osteoarthritis.
Trauma:
Old people are more prone to accidents that lead to osteoarthritis, osteomyelitis, and septic arthritis.
Underlying Disease:
The patient suffers from Tuberculosis, AIDS, repeated respiratory infection, and diabetes susceptible to acute arthritis.
INFECTIONS:
Viral and bacterial infections are predisposing factors for acute septic arthritis.
Diet and Lifestyle:
Smoking and alcohol addiction in susceptible individuals leads to rapid progression of arthritis e.g. Rheumatic arthritis, Gout.
Obesity, lack of exercise, and eating unhealthy food, hormonal changes in women are responsible for the early onset of back pain, small and large joint pain with stiffness.
Diagnosis:
Pain in one or more joints, swelling, and stiffness, lack of joint movements leads to a diagnosis of arthritis.
Along with clinical manifestations, x-ray and blood tests are required for proper diagnosis.
Acute arthritis Clinical Diagnosis:
Pain and swelling of one and more joints with stiffness.
Associated with viral infections like Dengue and Chikungunya.
Pain persists for 2-4 weeks maximum.
A patient has a history of rheumatic arthritis and gout.
Chronic arthritis Clinical Diagnosis:
Osteoarthritis:
Pain and functional restriction of hip and knee joints. The onset of pain is slow. Pain aggravates by motion and rest relieves pain. Muscle weakness and wasting of muscles are associated symptoms. The patient is above 45 years old and has asymmetric walking.
Tenderness with pressure, muscular pain around the joint, crepitus noise in the joint during movements, restricted movements of the joint, and bone swelling around an affected joint are associated symptoms of osteoarthritis.
X-ray shows the severity of structural changes. ESR and CRP are normal in osteoarthritis cases.
Synovial fluid from osteoarthritic knee joints is viscous and turbid with CPPD and calcium phosphate depositions.
Rheumatic arthritis:
Pain, swelling, and stiffness of small joints of hands and feet, aggravated in the morning. Arthritis of 3 or more joints. Symmetrical hand arthritis. Duration of symptoms persists for more than 6 weeks.
Blood tests, serological tests, and x-rays are more helpful to confirm the diagnosis.
ESR and CRP( C-Reactive Protein) are raised along with increased anti-CCP antibody and RA factor.
X-ray shows periarticular osteoporosis after 6 months of onset. For early detection of bone erosions, MRI and Doppler’s ultrasounds are helpful.
Gout:
Pain and swelling of distal joint specifically great toe with red shiny skin.
For clear diagnosis identification of MSU crystals in aspiration fluid of joint, bursa, or tophus is required.
In acute gout, synovial fluid is turbid due to increased cell count while synovial fluid of chronic gout appears white due to high crystal loads.
Assessment of renal function, blood tests, and x-ray are required to detect any changes in uric acid and protein deposition, Increased ESR and Neutrophils during an acute attack of gout and X-ray are necessary to understand the total damage to joints.
Arthritis Management:
-Aims of the management of arthritis are pain control, optimizing joint function, modifying the disease process, and education about disease diagnosis, and prognosis to patients.
-Successful management completes when considering the patient as a whole and treating every patient individually. Every patient requires a different approach to his condition.
-To form a treatment for a patient consider the following things: the patient’s daily activities, and work. Risk factors and associated causative factors of the disease. Patient’s knowledge about arthritis and his history, family history, and what he tried previously for the same condition.
– Counseling patient and his family about the disease condition, prognosis, and treatment options.
– Exercises are an important part of treating arthritis. Aerobic fitness training helps in the long-term reduction of pain and disability. It encourages well-being and sleeps quality and benefits to controlling obesity and diabetes mellitus.
Local muscle strengthening exercises are beneficial for chronic arthritis. These exercises improve reduced muscle strength, coordination, and balance.
– Modified use of tools and machines at the workplace, and decreased sports activity help to the improvement of occupational arthritis.
– Use of shock-absorbing footwear with thick, soft soles and use of walking sticks useful to improve pain in feet, knees, hip, and back regions.
– Obesity is the leading cause of both acute and chronic arthritis. Counselling obese people regarding joint pain is necessary and advising them about weight loss.
– Physical therapy, hydrotherapy, and occupation therapy assessments are beneficial for long-term pain, and disability management.
– Local heat, ice packs, wax baths, and local external application induce muscle relaxation and temporary relief of symptoms.
– Splints give support and rest for painful joints and periarticular tissues. Avoid splint during prolonged rest.
– Orthoses are permanent appliances to reduce instability and excessive abnormal movements. E.g. wrist splint, knee orthoses, iron, T-straps for the ankle.
– Encourage patients to self-help techniques like yoga therapy for stress, increase pleasant activities, and reduce activities that induce pain.
Homeopathic Remedies for Arthritis – Best Medicines
Homeopathy remedies are useful for both acute and chronic arthritis.
For acute arthritis, present symptoms, causative factors, and aggravating factors are considered to prescribing medicine.
On the contrary, for a chronic arthritis patient’s disease history, family history, details of symptoms including causative factors, aggravating factors, and personal history (like thirst, sweat, likes dislikes, habits, nature, and allergic conditions) are important parts to treat the disease.
Following remedies are helpful for arthritis, every remedy has individual characteristics.
Actaea spicata
Agaricus Muscaris
Apis mellifica
Arnica
Benzoic acid
Byonia alba
Calcarea Carb
Caulophyllum
Causticum
Colchicum
Ferrum met
Iodum
Guiacum
Ledum pal
Rhus tox
Rhododendron
Stellaria
1.Aconite: – for sudden appearance of inflammation in joints
Sudden appearance of rheumatic inflammation of joints with pain after exposure to cold, dry winds and aggravates at night.
Dose and Potency: Aconite 200 repeated for 3-4 hourly till acute pain subsides.
2.Actaea Spicata: for arthritis in small joints
It is a rheumatic remedy for small joints, specifically wrist rheumatism. Tearing, tingling pain with gastric complaints and subacute gout.
Dose and Potency: Actaea spicata 3X or 30 three times per day for 4-5 days.
3.Agaricus Muscaris: for rheumatic pain in diagonal limbs
Especially suited for old people. Pain presents diagonally in the right hand and left leg region before a thunderstorm.
A patient complains of rheumatic pain in limbs while at rest. The movement of the body relieves the pain. Coldness of extremities like frozen legs , stiffness, and itching of toes with neuralgic pain is characteristic of arthritis.
Dose and Potency:
30 and 200, both potencies are useful. Prescribe 30 potency 2 times per day for chronic arthritis and 200 potency 3 times a day for acute pain.
4.Apis Mellifica: for synovitis and back rheumatism
This is a remedy for synovitis associated with burning, stinging, throbbing pain and for rheumatism of the back and extremities with stiffness, itching, and swelling.
Complaints aggravated in hot weather and application of heat.
Dose and Potency:
Lower potency like 6x, mother tincture is helpful for synovitis. Prescribe 4 globules of 6x, three times per day for 2 weeks and 5 drops of mother tincture 3 times a day for 15 days.
5.Arnica Montana: for traumatic injuries and gout pain after physical exertion in cold, damp weather
It is a wonderful medicine for traumatic injuries. This has a great help in gout cases where fear of being touched or approached is presently associated with bruised, beaten feeling.
Exacerbation of acute rheumatic pain with soreness after muscular strain work during cold, damp weather.
Dose and Potency:
Can prescribe Arnica in 30, 200 and 1M doses depending on pain severity. If pain is severe, then give 200 or 1M doses of 4 globules every 2 hourly.
6.Belladonna: Severe sudden pain in hip after sitting for long hours
It is useful for severe sudden acute pain. Violent severe pain from joints of feet to hip region after sitting in one place for long hours like sitting in flight. Walking relieves pain.
Dose and Potency:
Belladonna 200 and 1M, 3-4 times per day is useful for acute severe pain.
7.Benzoic acid: for gout, rheumatic arthritis with urinary symptoms
This remedy is indicated for gout, and rheumatism associated with urinary symptoms.
It is useful for acute gout cases: Redness and swelling of the big toe aggravate at night.
It acts on rheumatism and osteoarthritis of the knee and tendo-Achilles.
Dose and Potency:
Useful in lower potency like 3x, 6x and 30; 3 times per day for 3-4 days.
8.Bryonia alba: for osteoarthritis and acute swelling of great toe, wrist, hip and knee joint.
Osteoarthritis of the knee, and hip with weakness, stiffness, heaviness, and weariness of limbs. Sudden pain with acute inflammation in the great toe, wrist, cracking in the hip joint, knee joint aggravated by exertion and touch. Pain relieved with pressure, bandage, and rest.
Dose and Potency:
Byonia alba is useful for chronic arthritis. Use in 30, 200 and 1M potency depending on severity of pain. 30 and 200 potency can be given 4 globules 3 times per day while 1M can prescribe once per week.
9.Calcarea carb: for old arthritis, rheumatic nodes and gout of knee.
It works for old arthritis, rheumatic nodes, and a gout of knee conditions.
Swelling and pain in knee joints, wrist, and fingers with coldness and profuse sweat are characteristic of Calcarea. Acute pain aggravated after exposure to wet.
Dose and Potency:
Use in 30, 200 and 1M potency depending on severity of pain. 30 and 200 potencies can be given 4 globules 3 times per day while 1M can prescribe once per week.
10.Caulophyllum: for rheumatic arthritis of small joints with nodes especially for women
It is a useful remedy for rheumatism of small joints like the wrist, hand, finger, ankle, and toes.
It is best for aching, cutting, and pain which changes place every few minutes. Finger joints have sore nodes.
This remedy is useful for rheumatic pain present in women after suppressed menses or during childbirth.
Dose and Potency:
Useful in 3x, 6x and mother tincture. 5 drops or 4 globules 3 times per day for severe pain.
11.Causticum: for osteoarthritis and rheumatic pains of knee
Rheumatic pains present in limbs which are ameliorated by warmth.
Osteoarthritis of the knee: Cracking and tension in the knee, pain stiffness at hollow of the knee which aggravates by sitting, rest while pain relieves with continued walking.
Dose and Potency:
Use in 30, 200 and 1M potency depending on severity of pain. 30 and 200 potency can be given 4 globules 3 times per day while 1M can prescribe once per week.
12.Colchicum: for acute gout and synovitis of small joints
This is an indicated remedy for acute gout as well as for muscular tissues, periosteum, and synovial membrane of joints, especially small joints.
Red, hot swelling, tearing pain of great toe that aggravates in evening and night. Acute exacerbation of gout is associated with great weakness, internal coldness, and a tendency to collapse.
Rheumatic pains present in the shoulder, wrist, hand, fingers, knee, ankle, and toes region with numbness. A patient complains of severe arthritis pain, such as screams with pain on touch.
Dose and Potency:
Useful in 30, 6x and mother tincture. 5 drops or 4 globules 3 times per day for severe pain.
13.Ferrum met: for rheumatic arthritis of shoulder joint
This is indicated for rheumatism of the shoulder joint in anemic people.
A patient complains of tearing, shooting pain in the right shoulder with cracking sounds, and pain in the right deltoid region. They are unable to raise their hands above their heads.
Dose and Potency:
Use in 30 and 200 potency depending on severity of pain. 30 and 200 potencies can be given 4 globules 3 times per day.
14.Guaiacum: for arthritis of upper extremity
It is a wonderful remedy for arthritic affection of the shoulder, arms, and hands.
Growing pricking pain, contraction of muscular tissue, and stiffness of joints with loss of muscular mass are characteristic of Guaiacum arthritis.
Dose and Potency:
Useful in 3x, 6x and mother tincture. 5 drops or 4 globules 3 times per day for severe pain.
15.Iodum: for rheumatoid arthritis associated with heart infection
This is indicated in rheumatism associated with sexual organ disease or with a heart infection.
Painful inflammation, swelling of knee joints, synovitis of small joints with trembling and tearing pains that aggravate at night.
Dose and Potency:
Useful in 3x, 6x and 30. 4 globules 3 times per day for severe pain.
16.Ledum pal: for gout of great toe and rheumatic pain in lower limbs radiates upwards
Rheumatic pain starts in the lower limbs and radiates upwards.
Gouty pain in small joints, both great toes with swelling, redness, hot, pale associated with stiffness, paralytic weakness, reddish discoloration of lower legs; rest and cold relieves pain.
Dose and Potency:
Useful in 3x, 6x, 30 and 200. 4 globules 3 times per day for severe pain.
17.Rhus tox: for acute and chronic rheumatic pain
This remedy is useful for acute and chronic rheumatic pains of joints from a sprain, over lifting, physical exertion, and getting wet.
Stiffness and pain of joints in the early morning after waking up but slow movements relieve pain.
Dose and Potency:
Use in 30, 200 and 1M potency depending on severity of pain. 30 and 200 potency can be given 4 globules 3 times per day while 1M can prescribe once per week.
18.Rhododendron: for rheumatoid and gout condition aggravates in summer.
This is a wonderful remedy for rheumatoid and gouty conditions during the hot season. Especially acute pain aggravated before a storm.
Acute inflammation, swelling of small joints, fibrous tissue associated with tearing pain, paralytic weakness of upper and lower limbs after slight exertion and at night.
Dose and Potency:
Useful in 3x, 6x and 30. 4 globules 3 times per day for severe pain.
19.Stellaria Media: Sharp, shifting, rheumatic pains all over body with stiffness
It is a specific remedy for acute and chronic rheumatism conditions.
Sharp, shifting, rheumatic pains all over body parts with a stiffness of joints. Condition aggravates in the morning and after motion.
Dose and Potency:
Useful 2x and mother tincture potency. 4 globules 3 times per day for severe pain along with massage of joints with mother tincture.
Remember that homeopathic remedies should be prescribed based on individual symptoms and characteristics. It’s crucial to consult with a qualified homeopath for proper evaluation and personalized treatment. Homeopathy focuses on treating the whole person, so a detailed case study is necessary to select the most appropriate remedy.
Homeopathic medicines should be taken only when prescribed by a homeopathic physician. Self-medication may aggravate the original conditions.