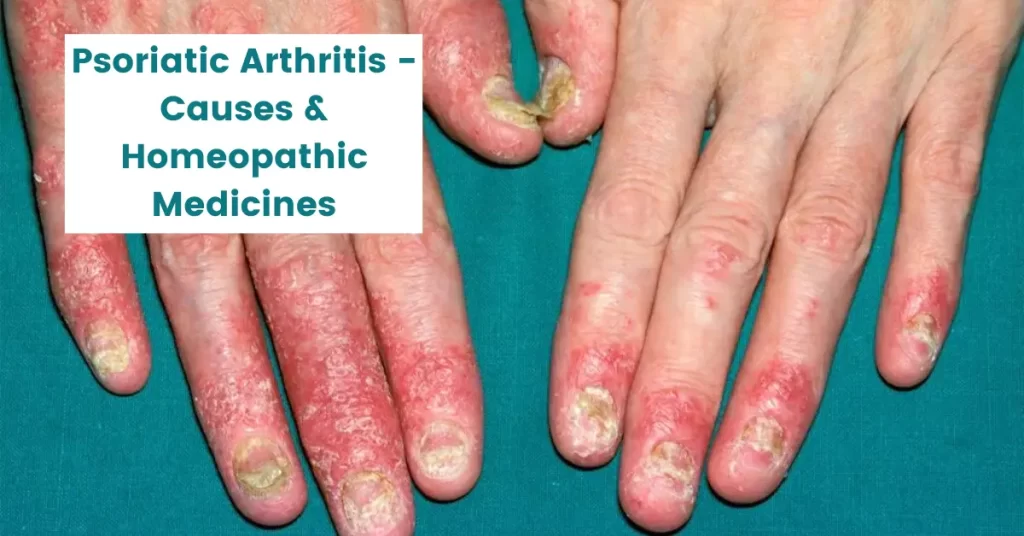
Psoriatic arthritis as the name suggests, it is an arthritis condition associated with psoriasis. Psoriasis is a skin disease. It is known as an autoimmune skin disease.
Not everybody has psoriasis suffers from arthritis. The exact causative factor of psoriatic arthritis is unknown. Only 7 % of patients who has psoriasis and can develop arthritis.
The occurrence of psoriatic arthritis is different for every individual. In some cases, arthritis occurs first and then psoriasis appears on the skin or vice versa. In some cases, both conditions appear simultaneously.
This condition is characterized by intermittent exacerbation depending on the trigger factors. It is an incurable disease, but regular treatment helps to limit the progression of the disease; reduce inflammation and pain in the joints.
Skin, small joints, large joints, and nails are involved in this condition. Depending on the joint’s involvement, Psoriatic arthritis is divided into three major types.
Types of Psoriatic Arthritis:
Along with skin, joints and nails are involved in psoriatic arthritis. In 40% of cases, small joints of hands and feet are involved along with one large joint like the knee and elbow. In 25 % of cases, symmetrical involvement of joints is there.
Depending on joints involvement, psoriatic arthritis is divided into three types:
1: Asymmetrical inflammatory Oligoarthritis:
In this condition, small joints of the hands or feet are involved. 40% of cases reported with this condition.
A gpatient complains of synovitis and periarticular inflammation along with affected joints. It affects hand fingers and gives a ‘sausage digit’ appearance to the middle finger.
In rare cases, large joints like the elbow and knee are affected by psoriatic arthritis.
2: Symmetrical Polyarthritis:
25 % of cases of psoriatic arthritis are involved in symmetric polyarthritis. As the name suggests, small and large joints of both hands and legs are involved in this condition.
It is predominant in women and is similar to Rheumatic Arthritis. But Rheumatic arthritis is characterized by nodules which are absent in Psoriatic arthritis. This condition is less painful and more benign.
3: Distal Interphalangeal joint arthritis:
It is an uncommon condition and more involved in men. This condition affects interphalangeal joints and surrounding tissues. A patient may complain of dystrophy of nails.
4: Psoriatic spondylitis:
It is a rare condition. The clinical features are like spondylitis but are associated with psoriasis.
5: Arthritis mutilans:
It is a complication of psoriatic arthritis. It is a deformative and erosive condition that affects fingers and toes. This condition destroys bones and cartilage.
It is a rare condition. It makes joints unstable.
Psoriatic arthritis Causes:
According to researchers, genetic factors, immunity, and infective factors are responsible for psoriatic arthritis.
Hereditary/ Genetic factors:
A family history of psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis plays an important role to produce psoriatic arthritis in a person.
If a person has a family history of psoriasis and arthritis, he is susceptible to psoriatic arthritis. Just some environmental triggers like allergic conditions and viral infection can be responsible to produce psoriatic arthritis.
Immunity:
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease condition. Immunity plays a significant role in arthritis and psoriasis also. If a person has low immunity power and has a family history, then he is susceptible to psoriatic arthritis.
Autoimmunity condition produces inflammation of joints and overproduction of skin tissue around infected joints.
Just a viral or bacterial or viral infection trigger is enough to produce the psoriatic arthritis condition.
Trauma:
Trauma to the skin, viral infection, and bacterial infection may be causative factors in some cases. A patient who has a family history of psoriasis are more susceptible to psoriatic arthritis.
Psoriatic Arthritis Symptoms:
As mentioned earlier psoriatic arthritis affects the skin, joints, spine, and nails. There are major signs and symptoms:
Skin eruptions:
Psoriatic arthritis presents with itchy scales, patches, and dryness of the skin. Dryness presents all over the body or specifically at the upper and lower extremities only.
Swollen fingers and joints:
Small joints like interphalangeal joints, fingers, and toes are involved most of the time. Psoriatic arthritis is associated with synovitis and inflammation of tissue surrounding joints.
A patient complains of swollen and inflamed fingers like Sausage. Large joints like the elbow and knee are also affected in some conditions. But large joint involvement is rare and benign.
Foot pain:
Extremities Psoriatic arthritis affects ligaments and muscles attached to joints also. It especially affects the heel region and foot joints.
Low back pain:
In rare cases, psoriatic spondylitis occurs. A patient complains of back pain.
Nail changes:
Extremities The characteristic symptom of psoriatic arthritis is the involvement of the nail. It destroys the structure of a nail. In some cases, rashes are appearing on the nail and surrounding the nail.
Eye infection:
Extremities A patient complains of eye infections like pain in eyes, dryness, and redness of eyes. A patient may develop a blurry vision.
Psoriatic arthritis symptoms have intermittent occurrence. A patient complains of on-and-off joint pain or periodic pain.
Signs and symptoms of rheumatic arthritis and psoriatic arthritis are the same but involvement of skin, and nail are characteristic of psoriatic arthritis. The presence of RA factor is a diagnostic criterion for rheumatic arthritis.
Risk Factors for Psoriatic Arthritis:
Age, immunity, trauma, and viral and bacterial infections are risk factors for psoriatic arthritis.
Age:
The occurrence of psoriatic arthritis is more predominant in middle-aged adults between 25 years to 50 years.
Immunity:
A person who has low immunity and a family history of psoriasis is more susceptible to psoriatic arthritis attacks.
Trauma:
Infection or trauma to the skin may trigger psoriasis tendency in a person. This trigger factor may lead to arthritis.
Psoriasis:
A person who is suffering from psoriasis has a great risk for psoriatic arthritis. Psoriasis is a great risk factor for arthritis.
Infections:
Any viral or bacterial infection may trigger psoriatic arthritis in a susceptible patient who has psoriasis.
Family and Personal History:
If a patient has a family history or personal history of psoriasis, then he is at high risk of psoriatic arthritis.
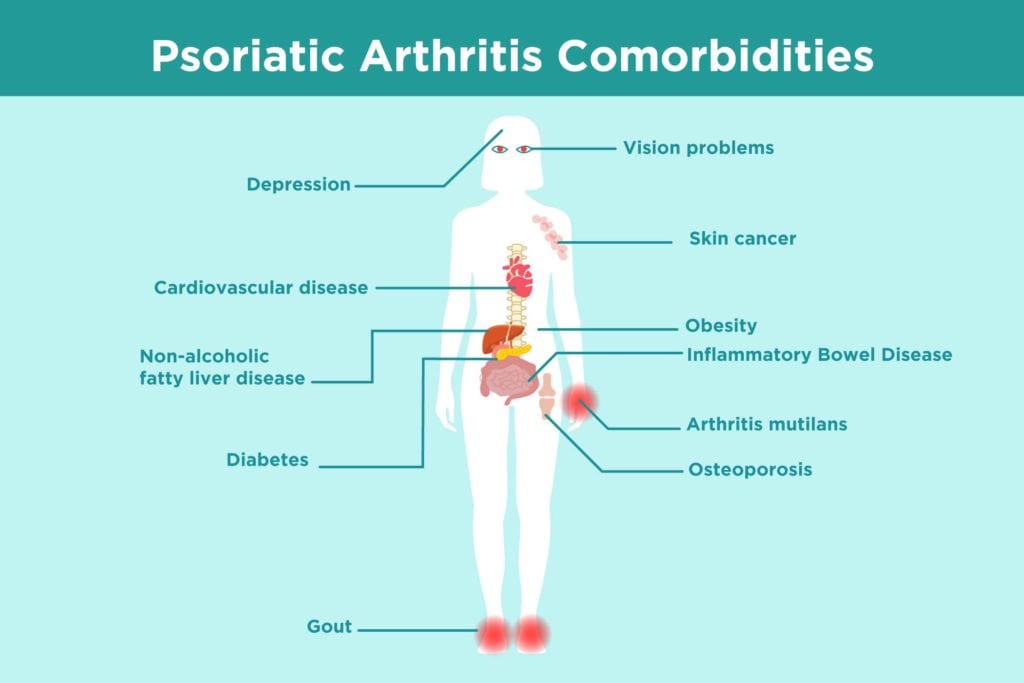
Diagnosis of Psoriatic Arthritis:
Psoriatic arthritis is a systemic disease. It involves the skin and musculoskeletal systems. Diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis depends on signs, symptoms, clinical features, and observation of a physician. There are no reliable diagnostic tests are available.
The patient has psoriasis or a family history of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. The patient complains of small joint pain or large joint pain with inflammation.
The patient has dryness, itchiness, and scales on the skin in patches. Joint pains and skin complaints are associated with brittleness or the destruction of nails.
The patient may complain of rashes, spots on the nail, and swelling of fingers. Sometimes patient states pain in the heel and sole region.
On clinical observations, a doctor may find pain in feet, and joints of extremities. The doctor can look for patches of skin rashes on the palm, shin, and elbow regions.
There are no blood tests are available for diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis, but RA factor test and joint fluid tests help to rule out rheumatic arthritis and gout.
X-ray and MRI help to diagnose bone and tissue changes in the upper and lower extremities.
Psoriatic Arthritis Management:
Psoriatic arthritis is an incurable disease condition. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder. There are limitations to the treatment.
Proper treatment management helps to reduce joint pain and swelling. A patient can reduce attacks of joint pain with help of drugs like NSAIDs. While the use of DMARDs (disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs) prevents the destruction of joints and bones. These drugs help to arrest further prognosis of psoriatic arthritis.
Physiotherapy and massage therapy help to reduce joint pain, back pain, and leg pain. But homeopathy has a great result in the treatment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
Homeopathy treatment reduces the chances of psoriatic arthritis in psoriatic patients. It helps to improve skin conditions and reduce joint pain.
Some lifestyle changes help to improve your life quality when you are suffering from psoriatic arthritis.
– Maintain a healthy weight appropriate to your age and height.
– Try to eat healthy food like fresh homemade food, fruits, and vegetables. Drink lots of water.
– Avoid smoking and alcohol.
– Keep yourself active. Do yoga, go for a walk, and do stretching exercises.
– If some environmental factors trigger your disease condition, then try to avoid those allergens like dust, food, etc.
The main goal of psoriatic arthritis management is ease of life and to improvement quality of life in psoriatic arthritic patients.
Best Homeopathic Medicine for Psoriatic Arthritis:
Homeopathy has a great sphere of action in psoriatic arthritis conditions. It is helpful to reduce swelling, inflammation, and pain in joints. It either reduces or halts rashes of skin in psoriasis.
Homeopathy is useful in acute conditions as well as in chronic tendencies of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. The remedy selection is dependent on the symptoms, personal history, and family history of a patient.
The patient who has a genetic history of psoriasis has great help with homeopathy to reduce the tendency of psoriatic arthritis. Before taking any homeopathy medicines, consult with a homeopathy physician.
Below are homeopathy remedies that are useful for psoriatic arthritis:
1: Arsenic Iod: For psoriasis and pain in a humerus
Arsenic Iod is suitable for the marked exfoliation of large scales, dry skin and itching. The itching aggravates after washing with cold water.
The patient complains of pain in the humerus after writing.
Dose and Potency: Arsenic iodum is useful in lower potency like 3x and 6x. Give 4 globules 2 times a day for 10 days.
2: Calcarea carb: psoriasis and sole pain
Calcarea Carb is good as a constitutional medicine. The patient who has a family history of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis will benefit from Calcarea carb.
The patient complains of pain in the hands, fingers, feet, ankle, and sole region. The soles are raw and dry. The patient has trembling in small joints, especially in the morning.
Dose and Potency: Calcarea carb 30 and 200 are useful. Give 4 globules of Calcarea carb 30, 2 times a day for acute pain. Calcarea 200; 4 globules once a week as a constitutional medicine.
3: China: Acute pain in limbs and joints with blue discoloration of the nail
Especially suited for pain in joints with swelling. The patient complains of great debility, trembling and numbness in extremities aggravates after movements.
Dose and Potency:
China 30 is useful for pain. Take 4 globules of China 30, 3 times a day for 5-7 days.
4: Dulcamara: useful for acute eruption alternate with arthritis
This is a remedy for suppressed eruptions which leads to arthritis. The patient complains of trembling of arms, swelling, and pain in small joints.
Dose and Potency:
Dulcamara 30 is useful for acute pain. Give 4 globules, 3 times a day for 7 days.
5: Graphites: Useful for toenail deformities and small joint pain associated with skin eruptions
It is a wonderful medicine for dry and cracked skin. The patient complains of brittle nails and deformity of nails, especially toes. The patient states acute pain in the toes and feet region.
Acute pain aggravates in the morning. Dryness of the skin and itching increase after exposure to heat.
Dose and Potency:
Use 4 globules of Graphites 30, 2 times a day for 7-10 days for acute pain. Use Graphites 200, 4 globules 2 times a week for 1 month as a constitutional medicine.
6: Ledum pal: Useful for acute pain in the lower extremities
It is useful for swollen ankles, foot pain, and sore heel. The patient complains of knee pain and lower leg stiffness. The patient has ascending pain from the feet to the thigh region associated with small joint swelling.
Dose and Potency:
Ledum pal 30 and 200 are useful for acute pain. Give 4 globules, 3 times a day for pain for 4 days depending on the severity of the pain.
7: Lycopodium: A constitutional remedy for psoriatic arthritis
Lycopodium acts best for pain in the hands and feet region. Acute pain associated with dryness of the palm and sole region. The patient complains of numbness of hands and feet; tearing pain in legs at night; and swelling and stiffness of knees.
The patient has a history of psoriasis. Brown spots appear here and there on the body, which increases after exposure to heat.
Dose and Potency: Lycopodium 30 is useful potency. Give 4 globules of Lycopodium 30, at night for 7 days.
8: Merc: It is indicated for the acute and severe condition of psoriatic arthritis
It is indicated for trembling of hands, pain, and stiffness in fingers and toes associated with deformity of nails. The patient complains of exfoliation of fingernails and moist itch-like eruptions on the hands.
Dose and Potency:
Merc cor 30, 4 globules 3 times a day for 7 days for acute pain of small joints.
9: Phosphorus: Useful for pain in small joints
It works wonderfully to reduce the tendency of acute pain in small joints in psoriatic arthritis. The patient complains of numbness and stiffness in fingers and arms in the morning.
Phosphorus has great help for small joint pain associated with knee and elbow pain.
Dose and Potency:
Phosphorus 30 is useful for acute pain. Give 4 globules of Phosphorus 30, 2 times a day for 5 days.
10. Phytolacca: Useful for an early stage of skin disease and rheumatic pain in the shoulder joint
It is indicated for popular and pustular lesions of the skin, especially in an early stage of skin disease.
The patient complains of shooting pain, stiffness, and neuralgia pain in the shoulder and arm regions. The patient states aching pain in the legs, hands, and toes.
Dose and Potency:
Phytolacca in lower potency like 6x, 12x and 30 are useful. Give 4 globules 3 times a day for 7-10 days.
11. Pulsatilla: Useful for joint pain in psoriatic arthritis
Pulsatilla is useful as a constitutional medicine to reduce the periodicity of joint pain in psoriatic arthritis. The patient complains of stiffness and redness of small joints. The patient feels numbness in the foot region.
The patient states dryness, heat, and itching in the sole and leg region.
Dose and Potency:
Pulsatilla is useful in 30C and 200C potencies. Take 4 globules, 3 times a day for 10-15 days in acute cases. Use Pulsatilla 200, 4 globules 3 times a week for chronic cases.
12. Psorinum: Constitutional medicine for psoriatic arthritis
Psorinum is prepared from the secretion of psoriasis eruption. It is a nosode. It is useful for a person who has a family history of psoriasis.
It is indicated for the weakness of joints associated with eruption around the fingernails. The patient has dirty skin with intolerable itching.
Dose and Potency: Psorinum 200 and 1M are useful remedies. But do take this medicine under the observation of a homeopathy physician only.
13.Sulphur: It helps to reduce the tendency of psoriatic arthritis
It is a constitutional medicine. It is useful for a person who suffers from psoriasis or acute arthritis. The patient complains of acute pain in small joints including wrists, interphalangeal joints, and toes associated with nail discoloration.
The patient complains of itching vesicles on the back of the hands. The patient has burning pain in the soles and palms, especially at night.
Dose and Potency: Sulphur is useful in lower potencies like 6c and 30C potencies. Give 4 globules of Sulphur 30, once a week depending on the severity of symptoms.
Remember that homeopathic remedies are prescribed based on individual symptoms and characteristics. It’s crucial to consult with a qualified homeopath for proper evaluation and personalized treatment. Homeopathy focuses on treating the whole person, so a detailed case study is necessary to select the most appropriate remedy.
Homeopathic medicines should be taken only when prescribed by a homeopathic physician. Self-medication may aggravate the original conditions.