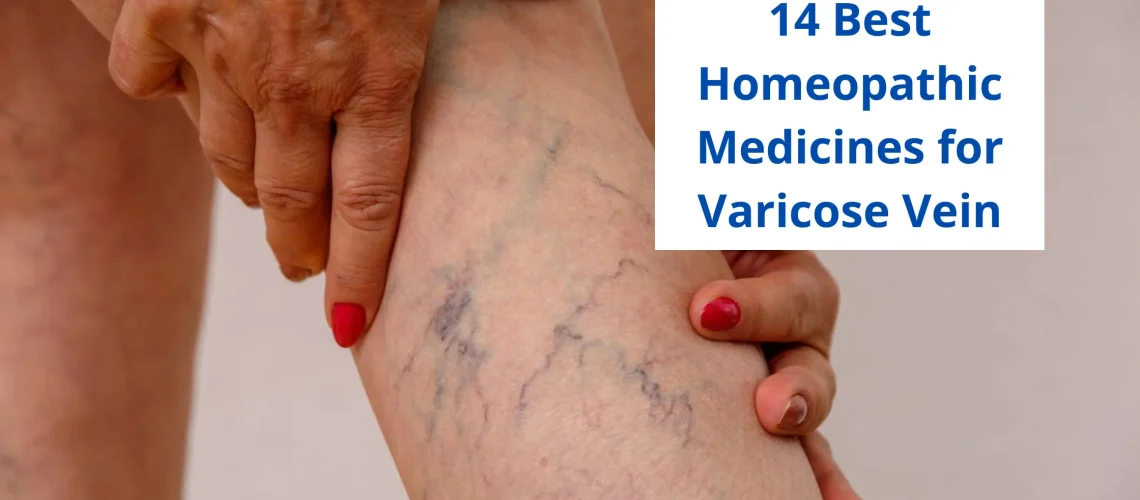
Varicose veins, with their twisted and bulging appearance, can not only be unsightly but also cause discomfort and pain. In the quest for relief, many turn to homeopathic medicine, a holistic approach that seeks to address the root cause of the condition. This blog explores the best homeopathic medicine for varicose veins, its causes, symptoms, risk factors, management and complete cure.
Homeopathy offers a range of remedies tailored to individual symptoms and constitution, aiming to alleviate pain, reduce swelling, and improve circulation without the side effects associated with conventional treatments.
By harnessing the healing properties of natural substances in highly diluted forms, homeopathic remedies aim to stimulate the body’s innate healing mechanisms. From Aesculus hippocastanum to Hamamelis virginiana, each remedy targets specific symptoms associated with varicose veins, offering a gentle yet effective approach to management and relief. Let’s explore the world of homeopathic medicine and its potential benefits in addressing varicose veins.
Table of Contents
ToggleHomeopathic Medicine for Varicose Veins
Unlock the natural and holistic potential of homeopathy in treating diseases and bodily disorders. Here, we explore a range of homeopathic medicines known for their effectiveness. The 14 best homeopathic medicine for varicose veins are as follows –
- Arnica montana
- Calcarea carbonica
- Hamamelis
- Pulsatilla
- Lycopodium
- Zincum metallicum
- Calcarea Fluor
- Calcarea Carb
- Fluoric Acid
- Apis Mellifica
- Graphites Naturalis
- Vipera Berus
- Millefolium Achillea
- Lachesis Muta
Arnica montana:
Overview: Arnica montana is a potent homeopathic remedy for varicose veins, especially when there is a sore, bruised sensation in the veins. It is indicated when there is a feeling as if one has been beaten, and the veins may exhibit bluish or blackish discoloration. Any exertion tends to worsen the condition.
Key Symptoms:
- Sore, bruised sensation in the varicose veins.
- Feeling as if one has been beaten.
- Bluish or blackish discoloration of the veins.
Calcarea carbonica:
Overview: Calcarea carbonica is highly effective for varicose veins that are painless, although a burning sensation may be present in some cases. This remedy is often indicated for individuals who are malnourished but obese, with cold hands and feet, and excessive sweating. It is particularly suited for those who feel chilly most of the time.
Key Symptoms:
- Painless varicose veins.
- Burning sensation in veins (in some cases).
- Malnourished but obese individuals.
Hamamelis:
Overview: Hamamelis is renowned for its effectiveness in managing varicose veins with a feeling of tiredness or aching in the legs. It is also indicated for varicose ulcers with stinging and pricking pain, as well as circular ulcers with high sensitivity. The remedy helps reduce the engorgement of blood in veins and alleviate related symptoms.
Key Symptoms:
- Tiredness or aching in the legs.
- Varicose ulcers with stinging and pricking pain.
- Circular ulcers with high sensitivity.
Pulsatilla:
Overview: Pulsatilla is a valuable homeopathic remedy for varicose veins, particularly during pregnancy. It addresses symptoms such as intense pain in the veins, heaviness or weariness in the legs, and symptoms that worsen in warm weather. Hanging down the lower limbs tends to exacerbate the complaints.
Key Symptoms:
- Intense pain in the veins.
- Heaviness or weariness in the legs.
- Symptoms worsen in warm weather.
Lycopodium:
Overview: Lycopodium is indicated for varicose veins characterized by drawing or tearing pains in the legs, often accompanied by a numb sensation. It is particularly suitable when symptoms worsen with prolonged periods of stillness, such as when the person is keeping still. Lycopodium is also indicated for individuals who are constipated and may have other skin problems.
Key Symptoms:
- Drawing or tearing pains in the legs.
- Numb sensation in the legs.
- Symptoms worsen with prolonged stillness.
Zincum metallicum:
Overview: Zincum metallicum is a valuable homeopathic remedy for varicose veins with a tight, congested feeling in the legs. It addresses symptoms such as tearing pain in the legs, restlessness, and a sensation of insects crawling over the skin (formication). This remedy is particularly suited for individuals who experience uneasiness and heaviness in the legs, especially with constant motion.
Key Symptoms:
- Tight, congested feeling in the legs.
- Tearing pain in the legs.
- Restlessness and formication sensation.
Calcarea Fluor:
Overview: Calcarea Fluor is highly recommended for varicose veins characterized by swelling and joint pains. It is effective in reducing the engorgement of blood in veins and improving blood circulation. This remedy is indicated for enlarged veins, hardened veins, and knotty veins on the lower limbs. Dry, cracked skin on the legs may also be present.
Key Symptoms:
- Swelling and joint pains.
- Enlarged, hardened, or knotty veins.
- Dry, cracked skin on the legs.
Calcarea Carb:
Overview: Calcarea Carb is an excellent remedy for painless varicose veins that appear as prominent veins on the legs. It is indicated when there is a burning sensation in the veins, and the individual experiences marked coldness in the feet. This remedy is well-suited for individuals who are malnourished but obese, with chilly tendencies and excessive sweating, particularly on the feet.
Key Symptoms:
- Painless varicose veins.
- Burning sensation in the veins.
- Marked coldness in the feet.
Fluoric Acid:
Overview: Fluoric Acid is valuable for treating varicose veins that worsen with warmth. It addresses symptoms such as painful varicose veins in the legs, which are exacerbated by warmth. This remedy is indicated for long-standing, obstinate cases of varicose veins, often accompanied by varicose ulcers with red margins. Pain in the ulcers is intense, and warmth exacerbates it, while cold applications provide relief.
Key Symptoms:
- Painful varicose veins worsened by warmth.
- Varicose ulcers with red margins.
- Intense pain in the ulcers.
Apis Mellifica:
Overview: Apis Mellifica is indicated for varicose veins characterized by stinging pains and burning sensations. It addresses symptoms such as swelling in the legs, burning sensation, and sensitiveness. This remedy is suitable for individuals who feel tired, bruised, and heavy in the lower limbs, with a tendency for swelling and inflammation of the veins.
Key Symptoms:
- Stinging pains and burning sensations.
- Swelling in the legs.
- Tiredness, bruised feeling, and heaviness in the lower limbs.
Graphites Naturalis:
Overview: Graphites Naturalis is a highly recommended remedy for varicose veins attended with itching. It effectively addresses symptoms such as itching in the veins, particularly worsening at night. This remedy is also beneficial for relieving cramping pains in the legs. Graphites Naturalis is well-suited for individuals who are obese, constipated, and may have other skin problems.
Key Symptoms:
- Itching in the veins, worse at night.
- Cramping pains in the legs.
- Obesity, constipation, and skin issues.
Vipera Berus:
Overview: Vipera Berus is indicated for varicose veins with a marked ‘bursting’ sensation in the legs. It effectively addresses symptoms such as severe cramping pain, swollen and tender veins, and blueness of the overlying skin. Elevating the legs provides relief from the symptoms. This remedy is well-suited for individuals experiencing intense pain and sensitivity in the affected veins.
Key Symptoms:
- Bursting sensation in the legs.
- Severe cramping pain.
- Swollen, tender veins with blueness of the skin.
Millefolium Achillea:
Overview: Millefolium Achillea is an effective remedy for varicose veins arising during pregnancy. It addresses symptoms such as drawing pain in the legs and varicose veins that easily break and bleed. This remedy is well-suited for both painful and painless varicose veins during pregnancy. Millefolium Achillea is beneficial for individuals experiencing discomfort and bleeding due to varicose veins during this period.
Key Symptoms:
- Drawing pain in the legs.
- Varicose veins that break and bleed easily.
- Varicose veins during pregnancy.
Lachesis Muta:
Overview: Lachesis Muta is an important remedy for varicose ulcers. It effectively addresses symptoms such as bluish-purple veins with thin, offensive discharge from the ulcers. This remedy is beneficial for individuals experiencing bleeding from the ulcers, intense burning sensation, and high sensitivity to touch. Warmth provides relief from the pain, and itching worsens after sleeping.
Key Symptoms:
- Bluish-purple veins.
- Offensive discharge from the ulcers.
- Bleeding, intense burning, and sensitivity in the affected area.
Varicose Veins Types
Varicose veins can manifest in different forms, each presenting unique characteristics and symptoms:
Primary Varicose Veins
These develop due to weak or damaged vein valves, leading to blood pooling in the veins. They often appear as twisted, bulging veins close to the surface of the skin.
Secondary Varicose Veins
Occur as a result of an underlying condition, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). They may be more severe and require specific treatment for the underlying cause.
Reticular Varicose Veins
These are smaller, bluish veins that often appear closer to the skin’s surface. While not as prominent as larger varicose veins, they can still cause discomfort and may indicate underlying venous insufficiency.
Telangiectasia (Spider Veins)
These are small, dilated blood vessels near the surface of the skin, resembling spider webs or tree branches. While typically not painful, they can cause cosmetic concerns and may indicate an increased risk of developing larger varicose veins.
Trunk Varicose Veins
These are larger varicose veins that affect the main superficial veins of the legs, such as the great saphenous vein or the small saphenous vein. They often cause more significant symptoms such as pain, swelling, and skin changes.
Varicose Veins Causes
Varicose veins develop when the valves within the veins weaken or become damaged, leading to blood pooling in the veins and causing them to swell and become enlarged. Several factors contribute to the development of varicose veins, including:
Genetics
A family history of varicose veins increases the likelihood of developing the condition. Genetic factors can influence the strength and integrity of vein walls and valves.
Age
As individuals age, the veins may lose elasticity and become weaker, increasing the risk of varicose veins.
Gender
Women are more likely to develop varicose veins than men, primarily due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy places increased pressure on the veins in the legs due to the growing uterus and hormonal changes. This can weaken vein walls and valves, leading to the development of varicose veins.
Prolonged Standing or Sitting
Occupations or activities that involve prolonged periods of standing or sitting can impair circulation and increase pressure on the veins, contributing to the development of varicose veins.
Obesity
Excess weight places added pressure on the veins, particularly in the legs and lower body, leading to the development of varicose veins.
Lack of Physical Activity
A sedentary lifestyle can weaken the muscles that support vein function, impairing circulation and increasing the risk of varicose veins.
Other Risk Factors
Other factors that may increase the risk of varicose veins include a history of blood clots, injury to the veins, and conditions such as chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) or deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Varicose Veins Symptoms
Varicose veins can cause a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild discomfort to more severe complications. Common symptoms associated with varicose veins include:
Visible Veins
One of the most noticeable symptoms of varicose veins is the appearance of swollen, twisted, or bulging veins that are visible just beneath the surface of the skin, typically in the legs or feet.
Pain and Aching
Many individuals with varicose veins experience pain, throbbing, or aching sensations in the affected areas, particularly after long periods of standing or sitting. The pain may worsen as the day progresses and improve with rest or elevation of the legs.
Heaviness and Fatigue
Varicose veins can cause a sensation of heaviness, tiredness, or fatigue in the legs, especially after extended periods of activity. This feeling may be accompanied by swelling or a sense of fullness in the affected limbs.
Itching and Discomfort
Some individuals with varicose veins may experience itching or discomfort around the affected veins, often due to inflammation or irritation of the surrounding skin.
Swelling
Swelling, or edema, is a common symptom of varicose veins, particularly in the ankles and lower legs. Swelling may worsen throughout the day and improve with rest or elevation.
Skin Changes
Over time, varicose veins may lead to changes in the skin surrounding the affected area, such as discoloration, dryness, or thinning of the skin. In severe cases, the skin may become red, inflamed, or develop ulcers or sores.
Restless Legs
Some individuals with varicose veins may experience restless legs syndrome, characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, especially at night. Restless legs can interfere with sleep and contribute to feelings of discomfort and restlessness.
Complications
In advanced cases, varicose veins may lead to more serious complications, such as blood clots, skin ulcers, or bleeding. It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience any concerning symptoms or complications associated with varicose veins.
Risk Factors for Varicose Veins
Several factors can increase the risk of developing varicose veins, including:
Age
The risk of developing varicose veins tends to increase with age, as the veins lose elasticity and become more prone to damage over time.
Gender
Varicose veins are more common in women than in men, possibly due to hormonal changes that affect vein elasticity and blood flow.
Family History
A family history of varicose veins can significantly increase the likelihood of developing the condition, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy can increase the risk of varicose veins due to hormonal changes, increased pressure on the veins from the growing uterus, and changes in blood volume.
Obesity
Being overweight or obese can put extra pressure on the veins, leading to weakened vein valves and increased risk of varicose veins.
Prolonged Standing or Sitting
Jobs or activities that involve prolonged periods of standing or sitting can impair blood circulation and increase the risk of varicose veins.
Lack of Exercise
A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to poor circulation and muscle weakness, both of which are risk factors for varicose veins.
Smoking
Smoking can damage blood vessels and impair circulation, increasing the risk of varicose veins and other vascular conditions.
Previous Vein Conditions
A history of blood clots or other vein-related conditions can predispose individuals to develop varicose veins.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes associated with puberty, menopause, or hormone replacement therapy can affect vein health and increase the risk of varicose veins.
Chronic Constipation
Straining during bowel movements due to chronic constipation can increase abdominal pressure and contribute to the development of varicose veins in the lower body.
Occupational Hazards
Certain occupations that involve heavy lifting, prolonged standing, or wearing tight clothing can increase the risk of varicose veins.
Genetics
Certain genetic factors may predispose individuals to develop varicose veins, such as abnormalities in vein structure or function inherited from parents.
Diagnosis of Varicose Veins
Diagnosing varicose veins typically involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Here’s how healthcare professionals diagnose varicose veins:
Medical History Assessment
Healthcare providers will inquire about the patient’s symptoms, medical history, family history of vein conditions, and any risk factors for varicose veins. Understanding the patient’s symptoms and medical background is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, the healthcare provider will visually inspect the legs while the patient is standing and sitting to assess for signs of varicose veins. They may look for swollen, twisted veins, skin discoloration, and other visible abnormalities. Palpation of the affected areas may also be performed to assess the texture and tenderness of the veins.
Doppler Ultrasound
Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test commonly used to diagnose varicose veins and assess blood flow in the veins. It uses sound waves to create images of the veins and evaluate blood flow direction, velocity, and any abnormalities in vein structure or function. Doppler ultrasound helps determine the location, extent, and severity of varicose veins.
Venography
Venography is a diagnostic procedure rarely used today due to the availability of less invasive imaging techniques like ultrasound. It involves injecting a contrast dye into the veins and taking X-ray images to visualize the veins and identify any abnormalities. Venography may be reserved for cases where ultrasound results are inconclusive or further detail is needed.
CT or MRI Scans
In some cases, computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be performed to provide detailed images of the veins and surrounding tissues. These imaging tests can help assess the extent of varicose veins, detect complications, and plan for treatment, especially in complex cases or when other imaging modalities are inconclusive.
Differential Diagnosis
During the diagnostic process, healthcare providers may also consider other conditions that can cause similar symptoms to varicose veins, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), chronic venous insufficiency, peripheral artery disease (PAD), or other vascular disorders. Differential diagnosis helps ensure accurate identification of the underlying condition and appropriate treatment planning.
Consultation with Specialists
In some cases, patients may be referred to vascular specialists or phlebologists (physicians specializing in vein disorders) for further evaluation and management, especially if the varicose veins are severe, recurrent, or associated with complications requiring specialized care. Collaboration with specialists ensures comprehensive evaluation and optimal treatment outcomes for patients with varicose veins.
Varicose Veins Management
Managing varicose veins involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, conservative measures, and medical interventions aimed at relieving symptoms, preventing complications, and improving vein health. Here are some key aspects of varicose veins management:
Lifestyle Modifications
- Regular Exercise: Engage in low-impact exercises such as walking, cycling, or swimming to improve blood circulation and strengthen leg muscles.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the veins and minimize the risk of developing or worsening varicose veins.
- Elevate Legs: Elevate legs above heart level whenever possible to alleviate swelling and improve blood flow.
- Avoid Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Take frequent breaks to avoid prolonged periods of standing or sitting, which can exacerbate symptoms.
- Compression Stockings: Wear compression stockings to provide external support to the veins, reduce swelling, and alleviate discomfort.
Conservative Measures
- Dietary Changes: Consume a high-fiber diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to promote healthy digestion and prevent constipation, which can exacerbate varicose veins.
- Hydration: Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water to maintain optimal blood volume and circulation.
- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbal supplements like horse chestnut extract or grape seed extract may help improve vein health and reduce symptoms.
Medical Interventions
- Sclerotherapy: Injection of a sclerosing solution into the affected veins to collapse them and reroute blood flow to healthier veins.
- Endovenous Ablation Therapy: Minimally invasive procedure involving the use of heat or laser energy to seal off diseased veins.
- Vein Stripping: Surgical removal of varicose veins through small incisions, typically reserved for severe cases or when other treatments fail.
- Ambulatory Phlebectomy: Surgical removal of varicose veins through tiny incisions, usually performed on an outpatient basis.
- Endoscopic Vein Surgery: Minimally invasive procedure using a tiny camera to visualize and treat varicose veins from within the vein.
- Laser Therapy: Use of laser energy to collapse and seal off varicose veins, often used in conjunction with other treatments.
Follow-Up and Monitoring
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor treatment progress, assess symptom relief, and address any complications or concerns. Patients should adhere to prescribed treatment plans, wear compression stockings as recommended, and make necessary lifestyle adjustments to optimize vein health and overall well-being.
Complications and Precautions
Seek prompt medical attention if experiencing severe pain, swelling, skin changes, ulceration, or other signs of complications associated with varicose veins. Avoid self-diagnosis and self-treatment, and consult healthcare professionals for personalized evaluation and management strategies tailored to individual needs and circumstances.
FAQs about Varicose Veins
What are varicose veins?
Varicose veins are swollen, twisted veins that often appear blue or dark purple. They usually occur in the legs and can be caused by weakened valves in the veins or increased pressure in the veins.
What causes varicose veins?
Varicose veins can be caused by factors such as genetics, age, pregnancy, obesity, prolonged standing or sitting, and hormonal changes. Weak or damaged valves in the veins can also contribute to their development.
What are the symptoms of varicose veins?
Symptoms of varicose veins may include bulging veins that are visible under the skin, aching or heaviness in the legs, swelling, itching, and cramping. In severe cases, skin ulcers or bleeding may occur.
Are varicose veins dangerous?
While varicose veins are generally not considered dangerous, they can cause discomfort and lead to complications such as skin ulcers or blood clots. It’s important to monitor them and seek medical advice if symptoms worsen.
How are varicose veins diagnosed?
Varicose veins are typically diagnosed through a physical examination and may require additional tests such as ultrasound to assess the extent of the condition and rule out other underlying issues.
What are the treatment options for varicose veins?
Treatment options for varicose veins include lifestyle changes, compression stockings, sclerotherapy, laser therapy, and surgery. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and individual circumstances.
Can varicose veins be prevented?
While some risk factors for varicose veins, such as genetics and age, cannot be controlled, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, avoiding prolonged standing or sitting, and elevating the legs can help prevent varicose veins from developing or worsening.
Are there natural remedies for varicose veins?
Natural remedies for varicose veins include herbal supplements, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise and avoiding tight clothing. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any natural remedies.
When should I see a doctor for varicose veins?
You should see a doctor if you experience symptoms such as pain, swelling, or skin changes associated with varicose veins, or if you have concerns about the appearance or progression of the condition. Your doctor can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Can varicose veins recur after treatment?
Yes, varicose veins can recur after treatment, especially if underlying factors such as genetics or lifestyle habits are not addressed. It’s essential to follow your doctor’s recommendations for lifestyle changes and ongoing monitoring to minimize the risk of recurrence.